Technology Backed by Scientific Studies
Information, researches, scientific papers and clinical studies from international health agencies and accredited institutions.
Health 101
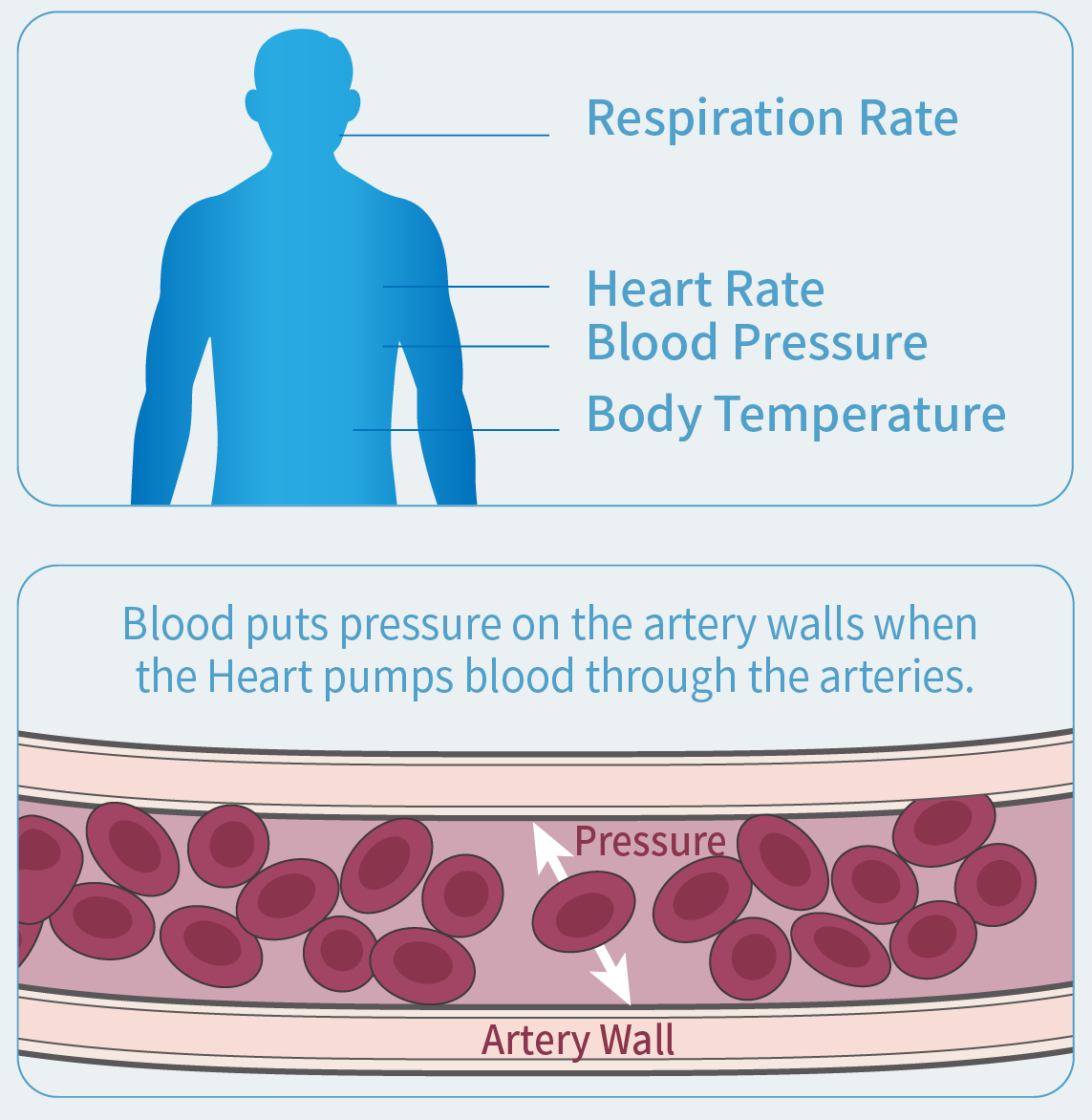
What is Vital Sign?
Vital Signs are measurements of the body's most basic functions such as heart rate, respiration rate, body temperature, and blood pressure.
Why monitor Vital Signs?
Vital Signs are useful in detecting or monitoring medical problems. (Source: Johns Hopkins University)

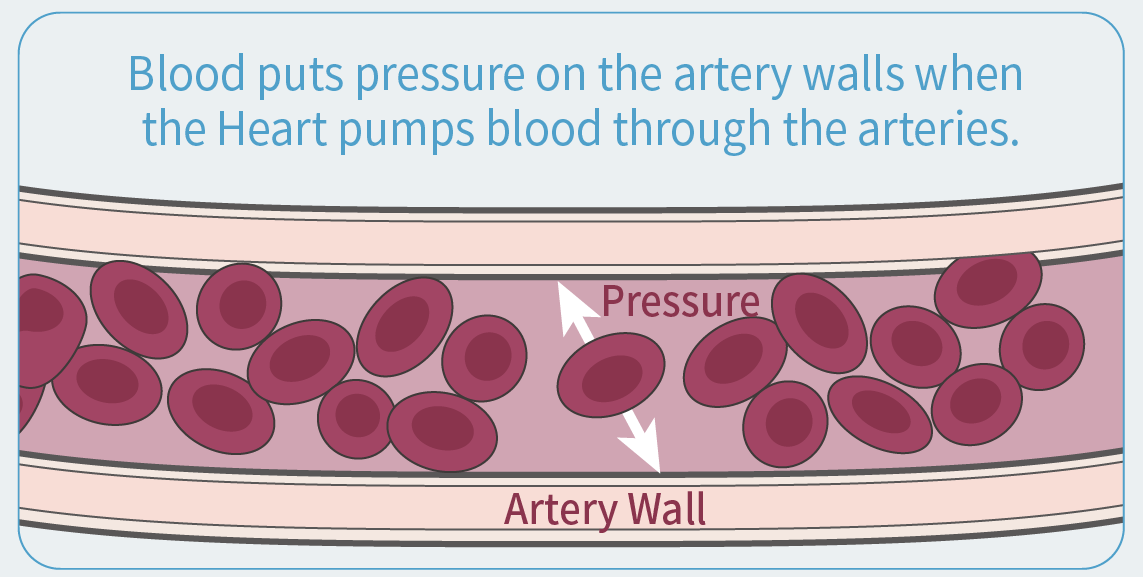
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the pressure of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. Arteries carry blood from your heart to other parts of your body.
What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can damage your heart and cause health problems if it stays high for a long time. (Source: US CDC)
What is heart disease?
The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type of heart disease in the United States is coronary artery disease (CAD), which affects the blood flow to the heart. Decreased blood flow can cause a heart attack.
What are the symptoms of heart disease?
Sometimes heart disease may be "silent" and not diagnosed until a person experiences signs or symptoms of a heart attack, heart failure, or an arrhythmia. When these events happen, symptoms may include:
Heart attack: Chest pain or discomfort, upper back or neck pain, indigestion, heartburn, nausea or
vomiting, extreme fatigue, upper body discomfort, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Arrhythmia: Fluttering feelings in the chest (palpitations).
Heart failure: Shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
What are the risk factors for heart disease?
High blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors for heart disease. About half of people in the United States (47%) have at least one of these three risk factors. Two several other medical conditions and lifestyle choices can also put people at a higher risk for heart disease, including:
- Diabetes
- Overweight and obesity
- Unhealthy diet
- Physical inactivity
- Excessive alcohol use

Scientific Papers
The principals and theories behind the technologies we use are backed up by the evidence based, peer reviewed studies published by accredited international science journals.

Piezoelectric Sensor for the Monitoring of Arterial Pulse Wave:
Detection of Arrhythmia Occurring in PAC/PVC Patients.

An Arterial Compliance Sensor for Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation
Based on Piezoelectric and Optical Signals.

Assessment of a calibration-free method of cuffless
blood pressure measurement: a pilot study.

Combining Local PWV and Quantified Arterial Changes for Calibration-Free
Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation: A Clinical Validation.

Clinical Trials
The most critical step to validate the performance, useability and safety of medical devices with international standards recognized by U.S. FDA., and eliminate possible issues before the release of our products.
International Standards Complied
ISO 81060-2: 2018
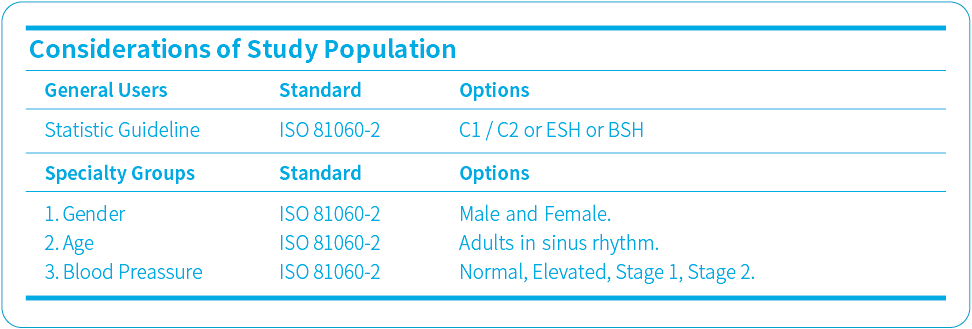
Demographics and characteristics
We covered multiple user groups include but not limited to: gender, age, and blood pressure.
Reference Sphygmomanometer
Welch Allyn DuraShock DS66 Trigger Aneroid
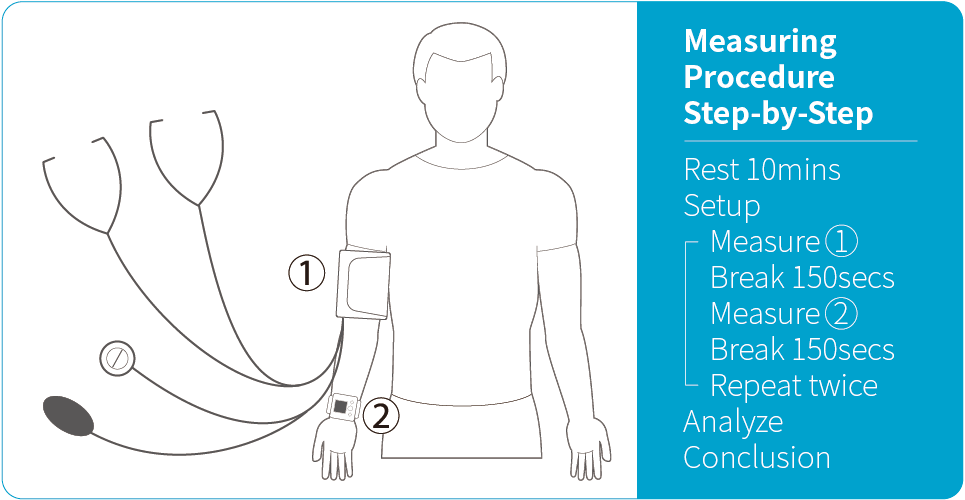
Measuring Procedure
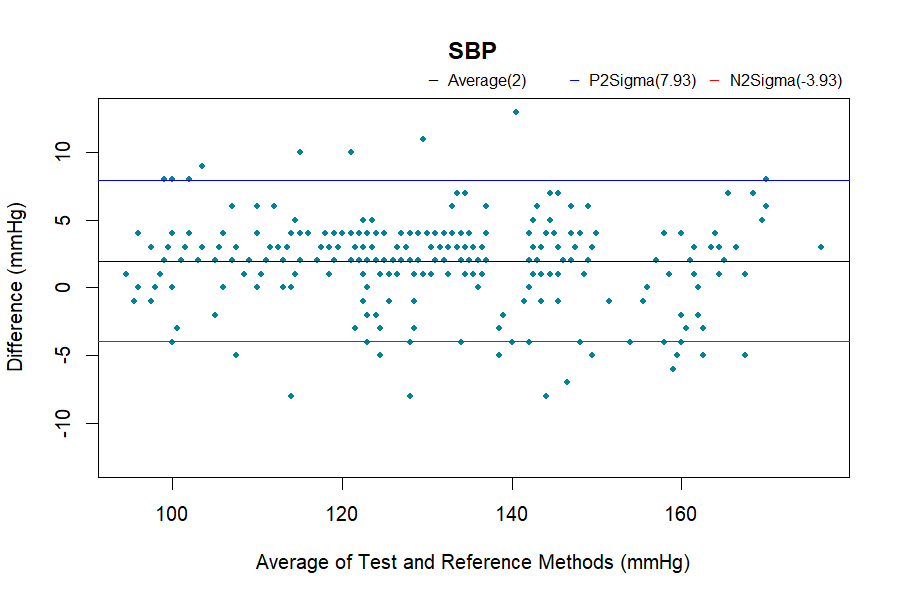
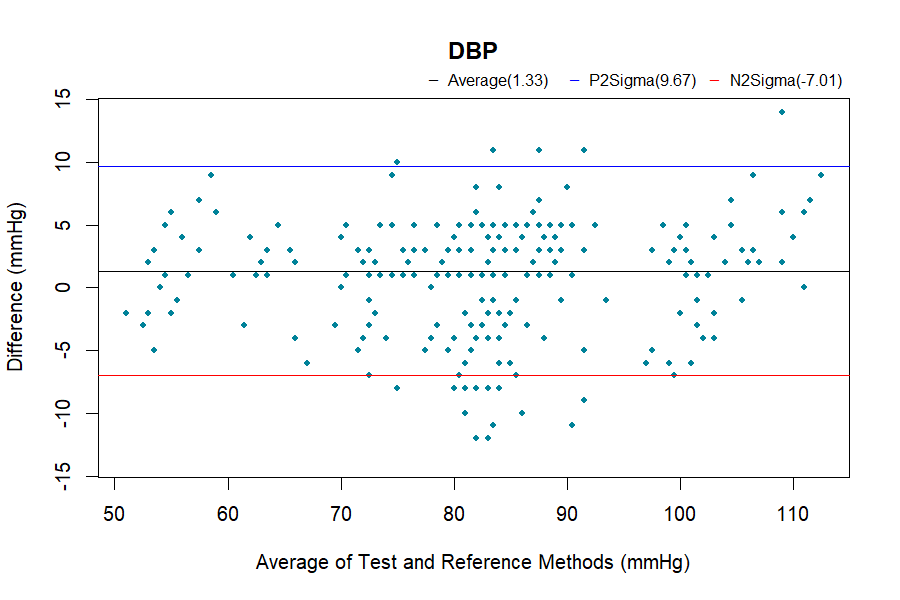
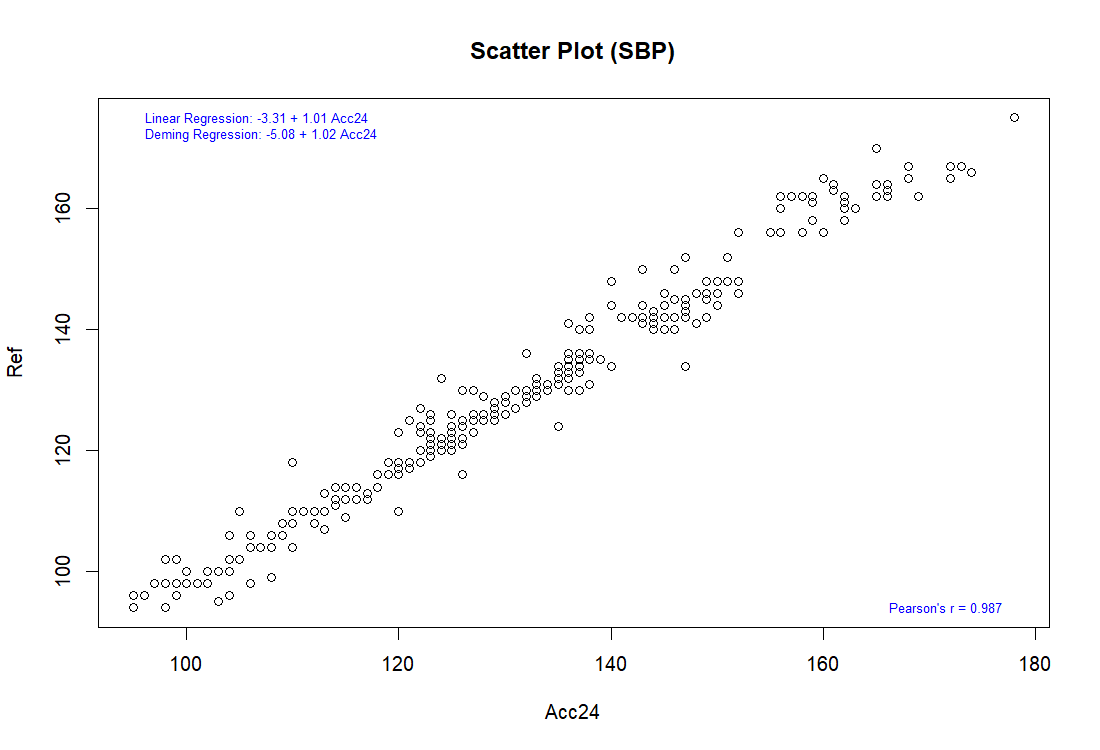
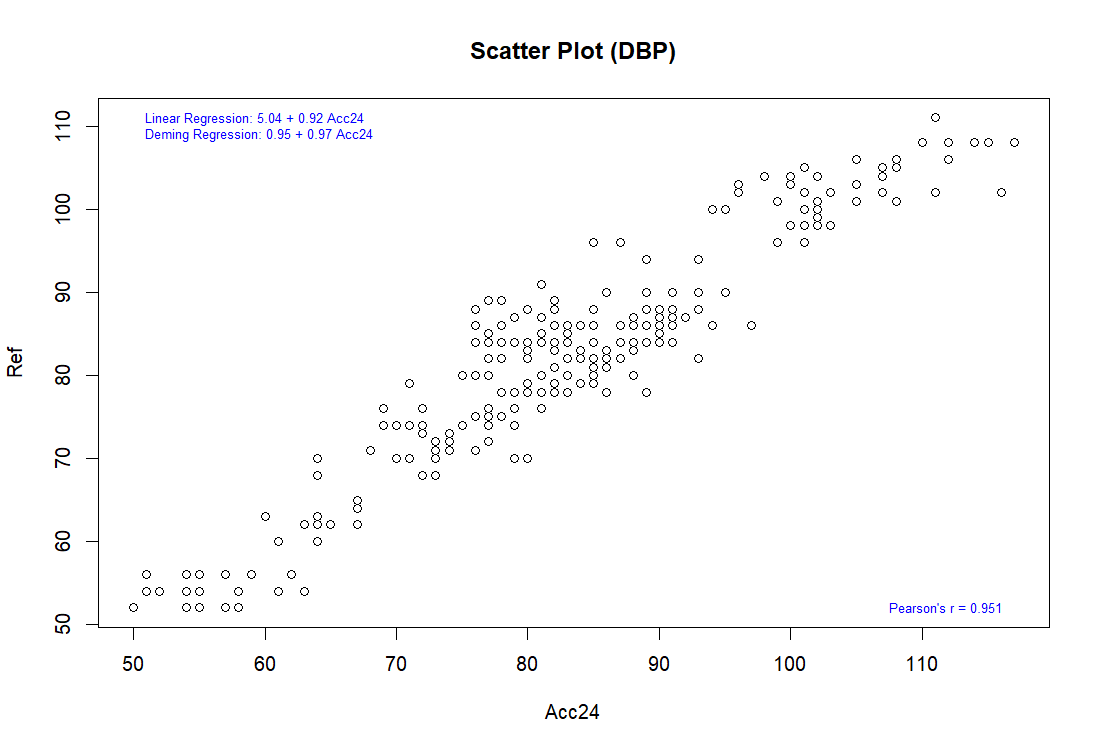
The procedure used in this study follows ISO 81060-2:2018 Clause 5.2.4.1.1. By compare results of reference and subject device using sequential method repeatedly to gain 3 sets of valid readings from the same arm of the same patient to minimal external interferes and change in the patient's physiological condition. In order to be considered as a valid set of blood pressure readings, the differences between the reference and our device should be within 12 mmHg for systolic, and within 8 mmHg for diastolic.
Analysis Methods
Bland-Altman analysis
Pearson correlation
Passing Criteria
The complete validation procedures should be conducted in at least total of 85 subjects, as specified in the ISO 81060-2 standards, with at least 255 BP determinations having a mean error magnitude ≤ 5 mmHg and a standard deviation ≤ 8 mmHg.
Results
General Group: Pass
Specialty Group: Pass



